By Dr. Douglas Green on May 28, 2025
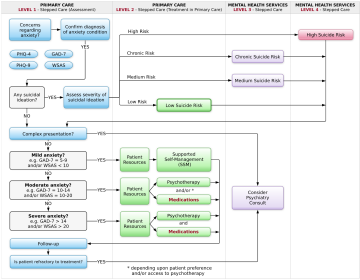
Studies indicate that anxiety conditions are often underdiagnosed and undertreated in primary care. The Ottawa Anxiety Algorithm has been designed to be evidence-based and practical, and contains guidance as to when and how to screen for and diagnose anxiety conditions, self-help resources that can be emailed to patients, links to community resources and treatment algorithms for the commonly used medications for these conditions.
By Dr. Katelyn Halpape on March 26, 2025
One in five Canadians live with chronic non-cancer pain (CNCP). Due to the historical role opioids had as a key component of CNCP treatment, a number of patients living with CNCP are on long-term opioid therapy (LTOT). I discuss the off-label use of buprenorphine/naloxone as a distinctive treatment option for CNCP and LTOT.
By Drs. Carson Chin, Nathan Hitchman, and Jordan Friedmann on January 24, 2024
Guidelines recommend that ULT be directed by SUA, but interpretation of such differs in acute and chronic phases of gout. Therapies require renal dose adjustment and can lead to serious and even fatal adverse events. Preventable adverse events continue to occur in BC due to underutilization of testing.
By Beata Chami on November 8, 2023
Experience of imposter feelings is linked to poor mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, and burnout and results in lower professional fulfillment. There may not be a “cure” for imposter syndrome, but there are strategies available to minimize the onset of it. Addressing symptoms that can have a significant impact on your well-being and those that you care for.
By Dr. Nawaaz Nathoo and Sorayya Seddigh on October 11, 2023
There are currently no eye drops for presbyopia treatment that have been approved for use in Canada. In December 2021, pilocarpine hydrochloride 1.25% eye drops became the first drug approved by the FDA for the medical management of presbyopia. Pilocarpine is a miotic agent that uses the eyes’ natural ability to constrict the pupil via parasympathetic innervation. It has been shown to improve near-intermediate vision without impacting distance vision.
By Dr. Sander Veldhuyzen van Zanten on August 9, 2023
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) continues to be an important pathogen, associated with peptic ulcer disease, dyspepsia, and gastric cancer. The conventional triple combination of a PPI, clarithromycin, and either amoxicillin or metronidazole is no longer recommended because its success rates have decreased to less than 60%. The recommended first-line therapy is concomitant therapy (PPI, clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and metronidazole) and second-line therapy is bismuth-based therapy (PPI, bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline).
By Drs. Kevin Lee and Persia Pourshahnazari on May 31, 2023
While not a fundamentally dangerous condition, CSU can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life and can be challenging to manage. Symptoms can be prolonged and can recur even after a long symptom-free period. Escalate and taper non-sedating H1-antihistamines, encourage daily antihistamine use, and add corticosteroids or refer to an allergist if needed.
By Drs. Rohit Vijh and Jason Wong on May 17, 2023
Pregnant persons should be screened for syphilis during the first trimester (or first prenatal visit), and at delivery (or any time after week 35 for those planning home births).
By Dr. Mark Adrian on April 19, 2023
Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal that can result in numbness, pain, and weakness of the lower extremities. Atypical presentations are common as are competing diagnoses. Top practice tips: distinguish the source of the symptoms, rule out competing disorders, send for imaging, encourage exercises that place the patient in a flexed position, and consider gabapentin, epidural steroid injections, and a referral for a surgical opinion.
By Drs. Kevin Lee and Persia Pourshahnazari on March 21, 2023
Despite being a fairly common problem, with an estimated prevalence of 0.5–5%, chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is often a challenging condition for health-care providers to diagnose and for patients to accept as a diagnosis. A diagnosis of CSU does not equate to a diagnosis of a systemic autoimmune disease. We do not routinely recommend dietary modification for CSU. We advise patients with CSU to limit alcohol intake and to take a higher dose of antihistamines prior to receiving vaccinations.
By Drs. Cheryl Young and David McVea on November 2, 2022
November is Radon Action Month. There are approximately 3,000 lung cancer deaths in Canada attributable to radon exposure each year, but there is limited awareness of radon both among the public and health care providers.
By Dr. Elisabeth Baerg Hall on October 19, 2022
October is ADHD Awareness Month. Until recently, female presentations of ADHD have been largely overlooked in both clinical and research settings. With increasing awareness and media attention to women and ADHD, adult women are asking if ADHD could explain their longstanding challenges.
By Drs. Angela Hu, Jon Chan, and Neda Amiri on May 24, 2022
Low back pain is a common complaint encountered in the general practitioner’s office. In fact, about two-thirds of adults suffer from low back pain at some point in their life, and it is second to only upper respiratory problems as a reason for visits to a physician. Axial spondyloarthritis is an autoimmune disease that results in inflammation in the spine. A number of therapies exist for this condition and early therapy may prevent progressive spinal fusion. Given the sheer prevalence of low back pain, identifying patients with axial spondyloarthritis can be challenging.
By Dr. Michael Diamant on April 19, 2022
The prevalence of ambulatory patients with advanced or end-stage heart failure (HF) is increasing over time, and now comprises as much as 14% of all patients with HF. Patients may be eligible for advanced therapies, including durable mechanical circulatory support (MCS) and heart transplantation, that can change their trajectory and markedly improve long-term survival.
By Shari Hurst on April 6, 2022
There are a few tips and tricks to improve medication tolerance and adherence, and improve quality of life for patients with HF-rEF. Multiple studies have shown that a focus on patient education and empowerment along with clinical follow-up for HFrEF medical treatment improves survival, reduces hospitalizations, and improves quality of life.
By Dr. Elisabeth Baerg Hall on October 27, 2021
October is ADHD Awareness Month. Patients may be increasingly aware of ADHD, having heard about the associated functional impairment and identifying with these stories. Treatment for adults with ADHD is effective. For best results, treatment includes both medications and Executive Function Skills support.
By Beata Chami on October 5, 2021
It has been eighteen months since COVID-19 emerged in Canada. The trajectory of the pandemic has placed a strain on our citizens’ mental health, particularly our frontline workers. While physician well-being has been a longstanding concern, the global pandemic has magnified the daily challenges that clinicians so bravely navigate to safeguard the health of their patients.
By Azin Ahrari, Neda Amiri, Mohammad Bardi, Natasha Dehghan on September 16, 2020
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common vasculitis in adults above 50 years of age. GCA is a rheumatological emergency. Rapid diagnosis and treatment are required to reduce the risk of complications.
By Drs. Nima Moghaddam, Christopher Cheung, Kenneth Gin on July 15, 2020
The debate over the optimal management in stable ischemic heart disease has grown over the past decade with more evidence supporting a conservative medical therapy approach over an upfront invasive strategy with coronary revascularization. However, there remains significant practice variation in deciding when to pursue coronary revascularization.
By Beata Chami on May 20, 2020
Healthcare professionals have been hit hard by the consequences of COVID-19. Some are putting in long hours, treating infected patients, and physically distancing themselves from their families. Others are losing work in their clinics and trying to figure out how to keep their practices afloat, all while worrying that they may be contracting the virus and putting their health at risk. This article will provide strategies and tools to support your well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic.
By Dr. Mary V. Seeman on February 5, 2020
Fellow psychiatrists often ask whether their patients with schizophrenia are aging prematurely. They point to the fact that several of their patients seem slowed down, forgetful, fidgety, and that they garble their words and stutter. These are, of course, all side effects of antipsychotic medication.
By Dr. Breay Paty on January 21, 2020
The therapeutic use of testosterone has increased dramatically in the last two decades. The reasons for this appear to be increased frequency of testing and marketing of testosterone replacement for middle-aged and older men. While men with unequivocally low testosterone levels usually benefit from hormone replacement, the risk/benefit ratio for men with equivocal (“borderline”) levels is not clear, especially men who desire fertility.
By Dr. Eileen Murray on October 16, 2019
Topical corticosteroids are the most frequently used topical medications for treating skin diseases. They are cheap, extremely efficacious and almost completely free of side effects when used appropriately.
By Dr. Alisa Lipson on September 25, 2019
Now in 2019, we are learning that the incidence in girls is higher than previously thought. The girls are catching up to the boys. What is that about? Turns out that the girls are better at hiding their disability but it is there. So, we have to look harder.
By Dr. Amin Javer on September 11, 2019
Sinusitis is a commonly encountered condition for the Canadian family physician. Chronic sinusitis has worse quality of life scores than COPD, CHF or angina. The total cost of diagnosing and treating sinusitis remains one of the most expensive chronic disorders experienced by the North American population and continues to increase yearly.
















Recent Comments